variable head permeability test ppt|constant head test vs falling : supermarket Variable head permeability test is one of several techniques by which the permeability of soil is determined. It is used to evaluate the permeability of fairly less previous soil. Permeability is the measure of the ability of soil to allow . 27 de out. de 2022 · Inscrição e registro do Free Fire Avançado já disponível no Brasil; passo a passo para se cadastrar no Advance Server FF APK 66.29.0 de novembro em 2022. Nesta quinta-feira 27 de outubro de 2022 a Garena abriu as inscrições para o Servidor Avançado Free Fire de novembro, o APK do Advance Server na versão .
{plog:ftitle_list}
web1xslots é confiável? Análise Completa & Bônus 2023 🎰. Cassino Online. ›. Resenha de cassinos. ›. 1xSlots Casino. 1xslots Casino: o cassino online com +10 mil jogos .
The coefficient of permeability depends on factors like particle size, pore water properties, degree of saturation, and soil structure. Laboratory tests like constant head and .Permeability depends on factors like particle size, void ratio, and degree of . Permeability depends on factors like particle size, void ratio, and degree of saturation. Darcy's law states that the rate of water flow through a soil is proportional to the .Variable head permeability test is one of several techniques by which the permeability of soil is determined. It is used to evaluate the permeability of fairly less previous soil. Permeability is the measure of the ability of soil to allow .
Darcy's law states that the rate of water flow through a soil is proportional to the hydraulic gradient. Common laboratory tests to measure permeability include constant-head and variable-head tests. Permeability is .Figure 12.7 Variable head tests in boreholes, (a) Falling head test. Water is added to the borehole to raise water levels, inducing flow from the borehole into the surrounding strata, (b) Rising head test.3) The procedures for conducting constant-head and falling-head permeability tests in the lab, including sample preparation, test setup, and calculations to determine k values. This .Permeability of a coarse grained soil can be determined by a constant head permeability test (AS1289.6.7.1-2001; ASTM D2434), and in a fine grained soil, falling head permeability test .
The constant head test method is used for cohesionless and more permeable soils (k>10-4 cm/s) and the falling head test is mainly used for cohesive or less permeable soils (k<10-4 cm/s). The constant head permeability method is .In the laboratory we employ two methods. One is constant head permeability test. And another one is Falling head or variable head permeability test. These tests measure the amount of water that goes through a soil sample in a fixed .Interpreting in Situ Variable-Head Permeability Tests - Free download as PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. Scribd is the world's largest social reading and publishing site.
5. Test Method There are four laboratory methods typically used for measuring the permeability coefficient: 1) the variable-head (falling-head) test 2) the constant-head test 3) the capillary method 4) back calculation from .One is constant head permeability test. And another one is Falling head or variable head permeability test. These tests measure the amount of water that goes through a soil sample in a fixed time interval. Constant head method is .6.4 Presentation of Results : The permeability values are reported at T0C and 270C. The state of sample is also reported in terms of water content, void ration and degree of saturation. 7. Video Constant Head Permeability Test Falling Head Permeability Test 8. Download Download PDF
The falling head method of determining permeability is used for soil with low discharge, whereas the constant head permeability test is used for coarse-grained soils with a reasonable discharge in a given time. For very fine-grained soil, capillarity permeability test is recommended. Usually, permeability of soils is determined by two methods:Constant Head - Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online. This document describes the procedure for conducting a constant head permeability test to determine the hydraulic conductivity (permeability) of soils according to ASTM D 2434. It discusses factors that influence permeability, Darcy's law, and .Figure 12.9 Analysis of variable head tests. For the generic case of a cylindrical test zone of length L and diameter D (Figure 12.11), where LID > 10 (as stated in BS EN ISO 22282-2:2012), permeability from variable head tests can be calculated as. where d is the diameter of the section of tubing within which the water level rises and falls. A material with continuous voids is called a permeable material. Hence permeability is a property of a porous material which permits passage of fluids through inter connecting conditions. There are two general types of permeability test methods that are routinely performed in the laboratory: 1) Constant head test method. 2) Falling head test .
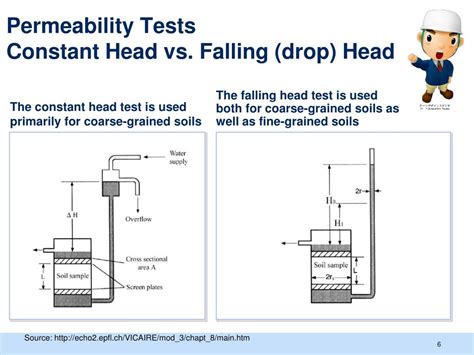
falling head vs constant permeability
SOIL PERMEABILITY PPT - Download as a PDF or view online for free. . Determination Of Coefficient Of Permeability Laboratory Methods Field Methods Indirect Methods Constant-head Permeability Test Variable-head Permeability Test Pumping-out Test Pumping-in Test Computation From The Particle Size From Consolidation Test Data .There are two general types of permeability test methods that are routinely performed in the laboratory: (1) the constant head test method, and (2) the falling head test method. The constant head test method is used for permeable soils (k>10-4 cm/s) and the falling head test is mainly used for less permeable soils (k<10-4 cm/s).tion of coefficient of permeability of soils using falling head and the constant head methods. This test is recommended for soils with coefficient of permeability in the range lo- 3 to 10-v cm/s and maximum particle size of 9.5 mm. 2. TERMINOLOGY 2.1 For the purpose of this standard, definition terms given inThe constant head permeability test is a laboratory experiment conducted to determine the permeability of soil. The soils that are suitable for this tests are sand and gravels. Soils with silt content cannot be tested with this method.The test can be employed to test granular soils either reconstituted or disturbed.
This document provides an overview of a laboratory class on permeability testing. It discusses: 1) The importance of permeability in geotechnical engineering applications and how it relates to settlement, earth dam design, slope stability, and more. 2) Hydraulic conductivity (k), which is a measure of soil permeability, and how it is determined using constant-head and falling-head .
Where, K27 = Permeability at 27°C KT = Permeability at T°C μ27 = Coefficient of Viscosity at 27°C μT = Coefficient of Viscosity at T°C. 5.5 Presentation of Results: The values of permeability at T 0 C and 27 0 C are reported. Also reported are corresponding void ration, degree of saturation and water content. 6. Falling Head Test
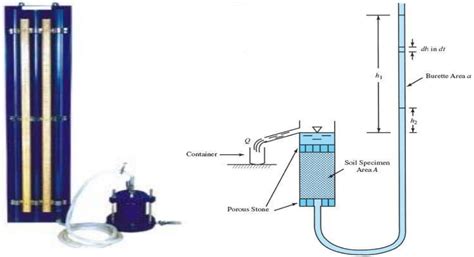
Constant Head Permeability Test. 2. Variable Head or Falling Head Permeability Test. These tests measure the amount of water that goes through a soil sample in a fixed time interval. Constant head method is suitable for coarse grained soils which are relatively more pervious because of their larger voids. While variable head is more suitable .8 Coefficient of Permeability Test No. Initial height of specimen Void ratio, e = (AL – Vs)/Vs Red. lower piezometer, h1 Red. upper piezometer, h2 Head loss, h Quantity of flow, Q Elapsed time, t Water temperature, C Viscosity correction factor, RT Distance between piezometers, LT Coefficient of permeability, K20 Soil Mechanics lab CE 350/01
The falling head method of determining permeability is used for soil with low discharge, whereas the constant head permeability test is used for coarse-grained soils with a reasonable discharge in a given time. For very fine-grained soil, capillarity permeability test is recommended. Usually, permeability of soils is determined by two methods: 1. This method, also called the Variable Head Permeability test, is suitable for fine grain soils with intermediate-low permeability such as clays and silts. . This test refers to the Constant head permeability method. At the .
This test method is used to determine the coefficient of permeability (K) having units of velocity or m/sec. Designation of the test; This test method has been standardized by American Association for State Highway and Transportation Officials under AASHTO – T – 215.
Falling variable head permeability test. Falling variable head method is a laboratory used method which is known as types of routine laboratory test that is mostly used in fine grained soil consisting the stand pipe of known area is inserted into the soil medium and water is allowed to flow through in order to noted the permeability of soil .
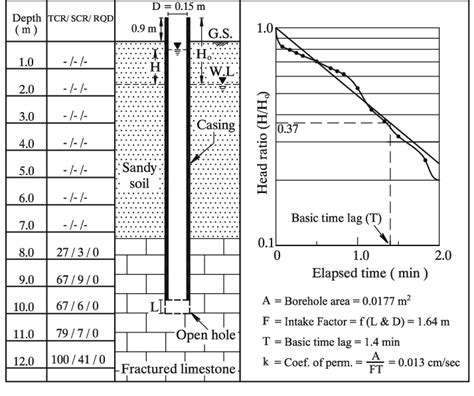
Interpreting in Situ Variable-Head Permeability Tests - Free download as PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free.Situation 1 For a variable head permeability test, the following data were given: Length of specimen= 37.5 cm; Area of specimen= 19.4 sq.cm; Coefficient of permeability= 0.002912 cm/sec. 2 points What should be the area of the standpipe for the head to drop from 63.5 cm to 30.5 cm in 8 minutes?The test method involves variable head (rising or falling) or constant head procedures and requires knowledge of the groundwater level. The type of test undertaken depends on the soil type. . The test measures the permeability (k) of the soil and because it is carried out in-situ provides a more reliable result than can be determined in the .
determining the coefficient of permeability and indeed the following laboratory methods are available for determining the value of k: • by constant water head test • by falling water head test, • by capillary permeability test, and • from a consolidation test. Rózsa (1977) rejects the laboratory method and recommends Test Method There are four laboratory methods typically used for measuring the permeability coefficient: 1) the variable-head (falling-head) test2)the constant-head test 3) the capillary method 4) back calculation from the consolidation test Generally, soils which contain 10% or more particles passing the No. 200 sieve are tested using the .
Variable-head permeability tests are often conducted in the field to determine local hydraulic conductivity values for soils. Many methods were developed over the years to interpret such tests.Constant head method – suitable for coarse grained soils. ii. Variable head method-suitable for fine grained soils. PERMEABILITY TEST – VARIABLE HEAD METHOD IS : 2720 (Part 17) - 1986. Aim: To determine the co-efficient of permeability of the given soil sample at desired density. by variable head method. Co-efficient of Permeability by Falling Head Permeameter. This test is suitable for fine-grained soils. The apparatus used for this test is called a falling head permeameter. The figure shows the diagrammatic representation of this test. The soil sample is kept in a vertical cylinder of cross-sectional area ‘A’ and length ‘L’.

lang deutz f3m2011 compression tester
falling head tests in borehole
WEBLatest draws and results for the US Mega Millions. Simulate playing the US Mega Millions. Pick 5 numbers from the main barrel and your Mega Ball and start playing.
variable head permeability test ppt|constant head test vs falling